Fiber Optics Overview
Two types, depending on the refractive index distribution between the core and the cladding.
Step index type and graded index type.
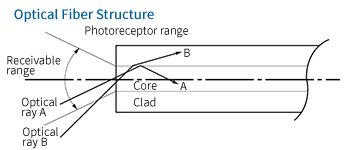
Optical fiber, also known as optical fiber, is a glass fiber with a thickness of about 0.1 mm, and is the main player in optical communication that transmits electrical signals such as video, audio, and various data. Since the core with a high refractive index is covered with a portion called a cladding with a low refractive index, light travels through the core portion by total internal reflection, enabling transmission with little loss even when bent. In addition, by increasing the capabilities of light emitting and light receiving elements, it becomes possible to transmit light pulses several hundred million times or more per second, enabling large amounts of information to be sent over long distances (compared to conventional copper cables). The amount of information transmitted is approximately 1,000 times that of the conventional method.) There are advantages such as less signal attenuation and resistance to noise caused by electromagnetic induction. Furthermore, due to the abundance of raw materials, it plays a leading role in current communication cables.
1
Since the transmission loss is small, long-distance transmission is possible.
2
Because of its high transmission bandwidth, large amounts of information can be sent simultaneously.
3
It is not affected by external induction or crosstalk.
4
Light does not leak from the optical fiber, so there is no external noise.
5
Since a single optical fiber is very thin, the cable can be made thinner. Many can be accommodated in a small space.
6
It is much lighter than copper cables.
kinds
Optical fibers are classified into two types according to the refractive index distribution between the core and the cladding.
There are four types of optical fiber, depending on the material used.
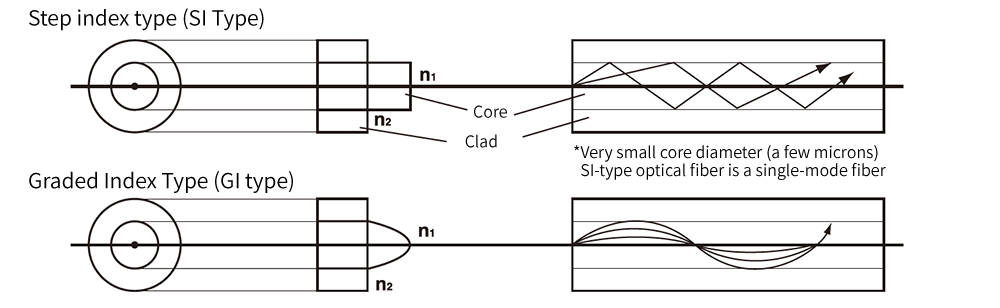
Both the core and the clad are made of quartz glass, and there are SI type and GI type. Especially when the core diameter is extremely small (9.5 mm), light passes only in the fundamental mode, and this is called a single mode fiber (SM type).
SM type fiber is suitable for long-distance, large-capacity communication, taking advantage of its low loss and broadband characteristics.
Both the core and the cladding are made of multi-component glass, making the most of their large diameter and high NA, making them suitable for intra-premises, short, and medium-range communications such as OA and FA. (SI type)
It uses quartz glass for the core and high-purity polymer for the cladding, and is suitable for medium-range communication such as OA and FA, taking advantage of its low loss and large aperture. (SI type)
High-purity polymethyl methacrylate resin in the core. A special fluorine-based polymer is used for the cladding, making it suitable for short-distance transmission at a low cost. When using (SI type)
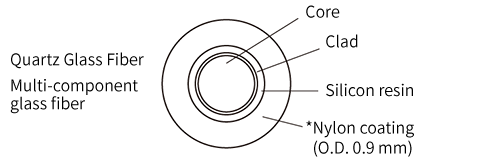
optical fiber, it must be in the form of an optical fiber cord or an optical fiber cable, but the core of the cord cable is a coated optical fiber with a diameter of 0.9 mm.
Cord structure
*Six colors of white, blue, red, yellow, green, and purple are available for coloring the nylon coating for core wire identification. * In addition to nylon coating, fluorine resin coating is also available.