- Q1. What is the star quad twist of the microphone cord?
-
When diagonal cores are used in a balanced line, the twisted structure can significantly reduce the effects of electromagnetic induction by canceling each other out.
- Q2. When laying multiple coaxial cords, are there any effects such as signal crosstalk between coaxial lines? Also, is there any influence of power lines?
-
In the case of coaxial lines, the power is small, so there is no effect, but if power lines are placed close to each other, there is an effect.
- Q3. To improve the sound quality of transmission, which factor is more effective, OFC conductors or thicker conductors?
-
Resistance value comes into play. It is better to use a conductor with a lower resistance, so it is effective to make the conductor thicker.
- Q4. What is the minimum bending radius of the cable?
-
For hard, fixed wiring like coaxial cables, it is best to consider 10 times the diameter as the minimum.
- Q5. What are the advantages of cross-linking?
-
Cross-linking strengthens intermolecular bonds, improves heat resistance, and improves solderability.
- Q6. How do you deal with environmental issues?
-
Eco-cables and lead-free products are available.
- Q7. Please tell me about the features of the mouse-proof cable.
-
Using the mouse's learning ability, we kneaded the karami component of hot pepper into the compound to prevent it from being bitten twice or three times.
- Q8. Do you have products that are resistant to cold and weather?
-
We are available for made-to-order manufacturing. See below for the cold-resistant
TUFRET.
- Q9. What is characteristic impedance?
-
It is the impedance for high frequencies seen from the sending end of an infinitely long coaxial cable.
- Q10. What is VSWR?
-
At the receiving end of a coaxial cable with a finite length, when a resistance different from that of the coaxial cable is connected, a reflected wave occurs and interferes with the traveling wave, generating a standing wave. The degree of matching between the coaxial impedance and the terminating resistance is generally called VSWR (standing wave ratio).
- Q11. What kind of cable constituent materials are there?
-
I will explain in detail below.
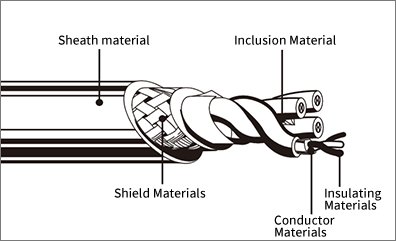
Material selection is an important factor in cable design.
We have a wide variety of construction materials to meet various conditions.
Conductor material
Electrolytic copper for general use (tough pitch copper)
Copper refined from electrolytic copper contains 0.02 to 0.06% oxygen and has been widely used as a conductor for electric wires since ancient times. Conductivity is 98-100%.
Oxygen-free copper (OFC)
Since the oxygen content is 0.001% or less, the electrical conductivity is improved (101-103%) and the resistance to hydrogen brittleness (copper becomes brittle when heated in high-temperature hydrogen). Broadcast cable conductors that are often used under severe conditions such as movement, bending, and twisting because they are superior in bending resistance, twisting resistance, and soldering resistance compared to general-purpose electrolytic copper. very suitable as In addition, it is highly expected to be used for audio and power cables in the future digital age, as it is recognized to have excellent sound quality.
Copper alloy (ALLOY)
It is an alloy wire made by adding various metals to copper.
Plating
Tin-plated (T)
Tin plating is applied to improve solderability and to prevent conductor corrosion.
Tin coat (TC-T; tin batch coating)
7 strands of each tin-plated conductor are twisted and coated with molten tin. It was developed mainly for plating for wrapping (winding) connections, but it is also suitable for crimping and soldering.
Solder plating (HP-A; solder batch coating)
Solder is plated to improve solderability.
Insulating material
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC, V)
It is widely used as an insulating material for the following reasons: 1) it has relatively good electrical and mechanical properties, 2) it is flame retardant, corrosion resistant, and water resistant, and 3) it is relatively inexpensive.
Crosslinked vinyl (XL-V)
The aforementioned PVC is irradiated with electron beams (sometimes chemically) to create a reticular molecular arrangement from an intermolecular arrangement, which improves the properties in terms of (1) greatly increasing the heat resistance temperature to 80-105°C, (2) greatly reducing deformation during soldering, and so on.
Polyethylene (E)
(1) Excellent electrical properties and chemical resistance (2) Excellent ozone resistance, water resistance, and weather resistance, and (3) Heat resistance and flammability.
Cross-linked polyethylene (HC-E)
The above-mentioned polyethylene is irradiated with electron beams, and the weak point of polyethylene, which is weak against heat, has been improved.
Expanded polyethylene (CE)
The dielectric constant can be varied by changing the degree of foaming, which has the following features: (1) For the same outer diameter, the capacitance can be lowered. However, there is a drawback that the mechanical strength is slightly reduced.
Cross-linked foamed polyethylene (HC-CE)
The above foamed polyethylene is irradiated with electron beams to improve heat resistance and mechanical properties.
Teflon (FEP)
It is an ideal organic material with excellent electrical properties, heat resistance, chemical resistance, and weather resistance.
Intermediate material
Interposition is not only a material that rounds out the cable, but is also closely related to the strength of the cable. The strength (especially tensile strength) of the cable changes greatly depending on the selection of the interposition. Typical intervening materials include the following.
cotton thread
Threads made by twisting a large number of threads taken from cotton are used.
jute
Twisted hemp threads are used.
piano wire
It is used as a messenger wire for hanging microphone cords.
Synthetic fiber
Various synthetic resin cords are used depending on the application.
Shahei (Shield)
braid
This is a shielding method with excellent flexibility and shielding effect, and is widely used in general. The most common materials used are (1) copper and (2) iron, etc. Three to ten strands of 0.1 to 0.2 mm dia. are alternately braided on the insulator.
horizontal winding
The annealed copper wire is made by winding a number of tinned annealed copper wires on an insulator in a helical shape, making terminal processing very easy. If bending resistance and twisting resistance are required, double winding (opposite directions) improves the characteristics.
tape winding
Copper, aluminum, aluminum-laminated polyester tape (polyaluminum tape), etc. is wrapped around an insulator in a helical shape. Although the shielding density is 100%, the cable tends to lose some flexibility compared to braided and horizontal winding.
conductive resin
The insulating material is coated with a conductive resin containing carbon (carbon) by extrusion, and the shielding effect is slightly lower than that of other metals.
Sheath material
Polyvinyl chloride (V)
Although it is basically the same as the insulation material PVC, the material composition is considered in terms of (1) improved wear resistance, (2) improved flexibility, and (3) improved weather resistance.
special grade;
●Rat-proof (RPC)
It is used to prevent rodent feeding damage. A rodent repellent mainly composed of the pungent component of chili pepper is encapsulated in microcapsules and kneaded with the wire coating material, so it is possible to protect against rodent damage for a long time.
●on-migratory (NR)
It is a formulation that does not cause color or contamination of compounding agents due to contact with other plastics.
●Non-toxic for medical use (M-PVC)
It is a formulation that clears voluntary standards for medical compounds.
There are also compounded products for oil resistance, flexibility, cold resistance, weather resistance, etc.
Polyurethane (PUR)
It is a synthetic resin with the characteristics of rubber, and has elasticity and excellent weather resistance, oil resistance, and wear resistance, but it has the disadvantage of high friction resistance.
TUFRET
Developed as a result of our many years of research, this sheath material has the features of both vinyl and chloroprene rubber, and is expected to be used in a wide range of fields in the future. 1It is superior to chloroprene rubber in terms of wear resistance, toughness, cold resistance, oil resistance, etc. 2It has the same performance as chloroprene rubber in terms of heat resistance, water resistance, elasticity, etc. A flame-retardant type of TUFRET (FR-TUFRET) is also available.
Comparison of TUFRET and conventional materials
|
TUFRET |
chloroprene rubber |
PVC |
Operating temperature
range (℃) |
-60 to +90 |
-40 to +80 |
-20 to +60 |
| Wear resistance |
◎ |
× |
△ |
| Oil resistance |
◎ |
○ |
× |
| toughness |
◎ |
○ |
△ |
| water resistant |
○ |
○ |
○ |
| Heat deformation resistance |
◎ |
◎ |
△ |
| Hardness (Shore A) |
80 |
67 |
82 |
(◎ > ○ > △ > ×)
back to index
